Introduction
Welcome to our journey of optimizing calendar performance! At the heart of every scheduling tool lies a complex web of algorithms and databases, working tirelessly to ensure that every meeting, appointment, and event falls seamlessly into place. However, what happens when these processes start to lag, causing frustration and delays for users? That’s where our story begins. Let’s dive into the journey of how we tackled latency and optimized costs for our calendar product’s most crucial API: the free-slot API.
The Challenge
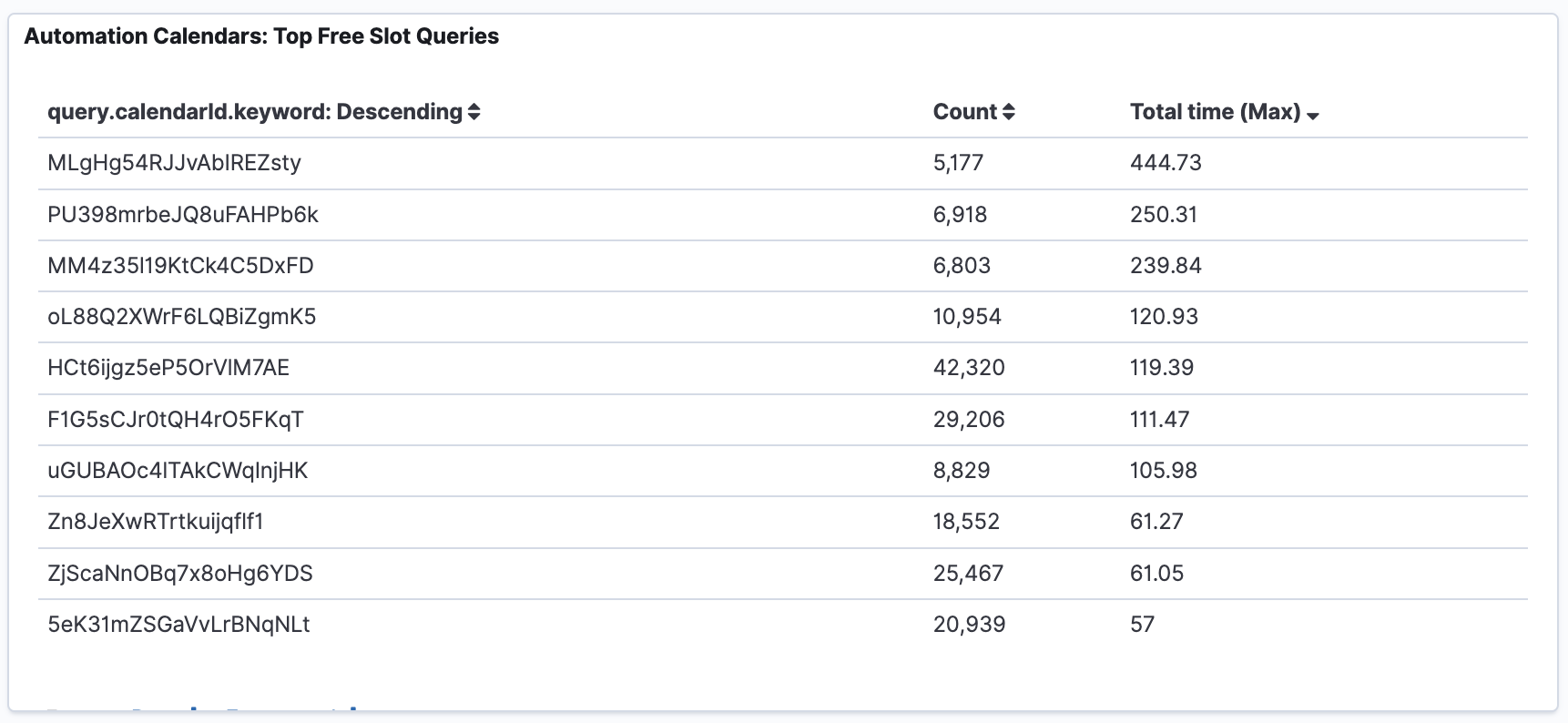
With median latencies hovering around 14 seconds and max latencies spiking up to a staggering 250 seconds, it was evident that significant improvements on the free-slot API were imperative. Refer to the video below to understand the issue we’re talking about.
Initiatives
Our initiatives were driven by a relentless pursuit of understanding and optimization:
- Code Refactoring and Optimization: We delved deep into the intricacies of our free-slot API, unraveling its complexities and streamlining its execution for improved efficiency.
- Firestore Index Optimization: Suspecting inefficiencies in our Firestore indexes, we fine-tuned them to alleviate latency burdens, guided by insights gleaned from query logs.
- Elasticsearch Integration: Leveraging Elasticsearch (ES), we offloaded certain functionalities from Firestore, shedding unnecessary burdens and streamlining operations, resulting in the removal of approximately 16 indexes.
- PoC with Elasticsearch: Exploring alternative data storage solutions, we conducted a PoC to evaluate the feasibility of powering our free-slot API with Elasticsearch, opening new avenues for optimization.
- Caching Strategies: Recognizing the potential of caching to mitigate latency, we experimented with various caching strategies to expedite response times.
Approach
Embracing setbacks and maintaining unwavering courage, we honed our approach to uncover underlying issues:
- Identifying Recurring Event Anomalies: Armed with a comprehensive understanding of our codebase, we discerned irregularities in handling recurring calendar events, setting the stage for deeper investigation.
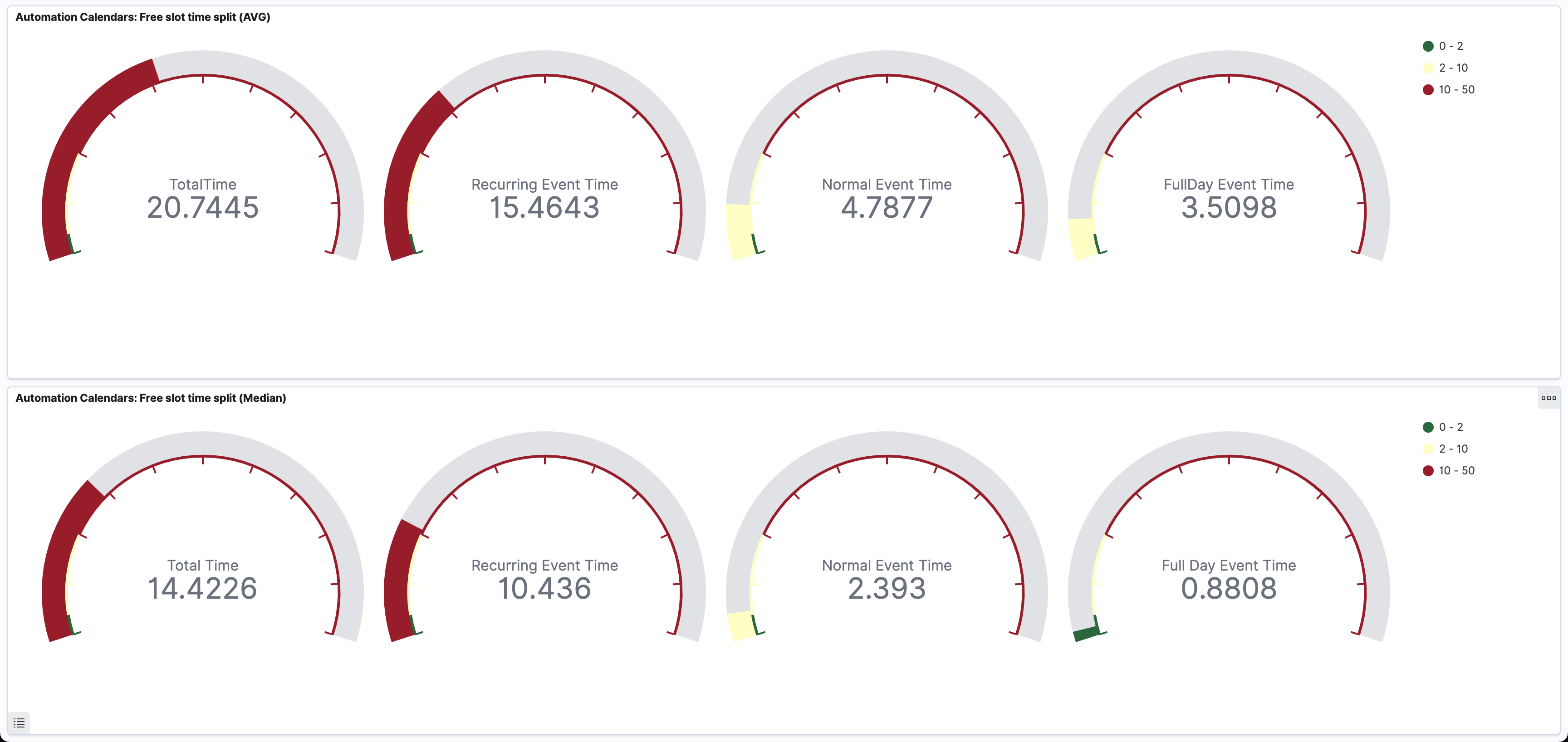
- Data Validation: Validating our suspicions with empirical evidence, we uncovered disparities in event reads, shedding light on the disproportionate impact of recurring events on latency.
| Event Type | Reads per Month |
|---|---|
| Recurring Events | 2.4 Billion |
| Normal Events | 1.3 Billion |
| FullDay Events | 799 Million |
- Assumption Verification: With a keen focus on performance optimization, we probed further to validate our assumption that latency correlated with the volume of records fetched.
The Eureka Moment and The Solution
- Understanding Recurring Events: Recurring events posed a unique challenge. Unlike regular events, we couldn’t run range queries on them. For instance, imagine you have a lunch event scheduled five years ago that still repeats. We couldn’t simply apply a start date query as we needed the original master event to generate current and future occurrences.
- Flagging Ended Calendar Events: Recognizing the prevalence of outdated events contributing to unnecessary latency, we implemented a solution to flag ended calendar events, mitigating the retrieval of obsolete data.
- Simplicity Wins: Sometimes, a simple tweak like adding a flag can work wonders.
The Impact
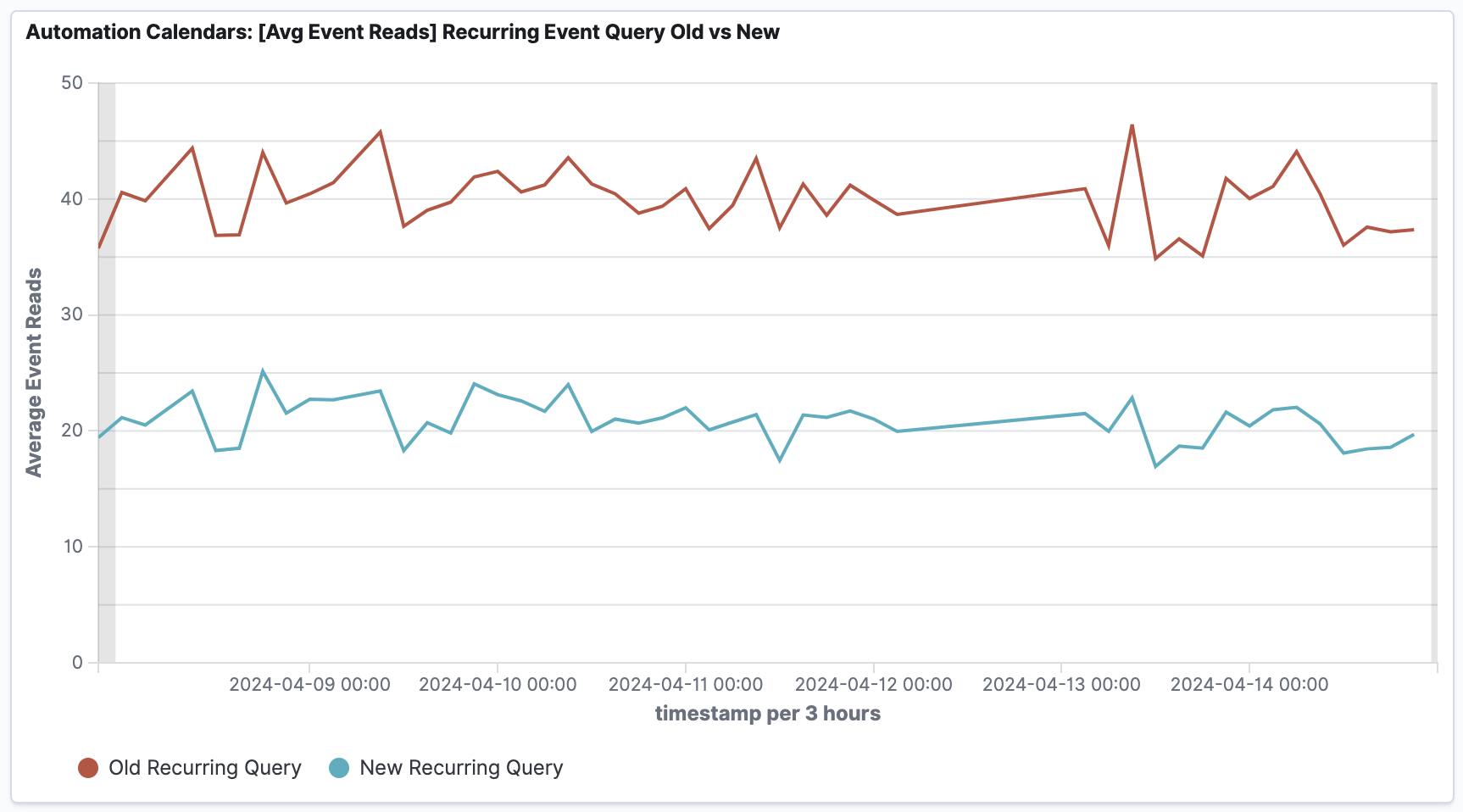
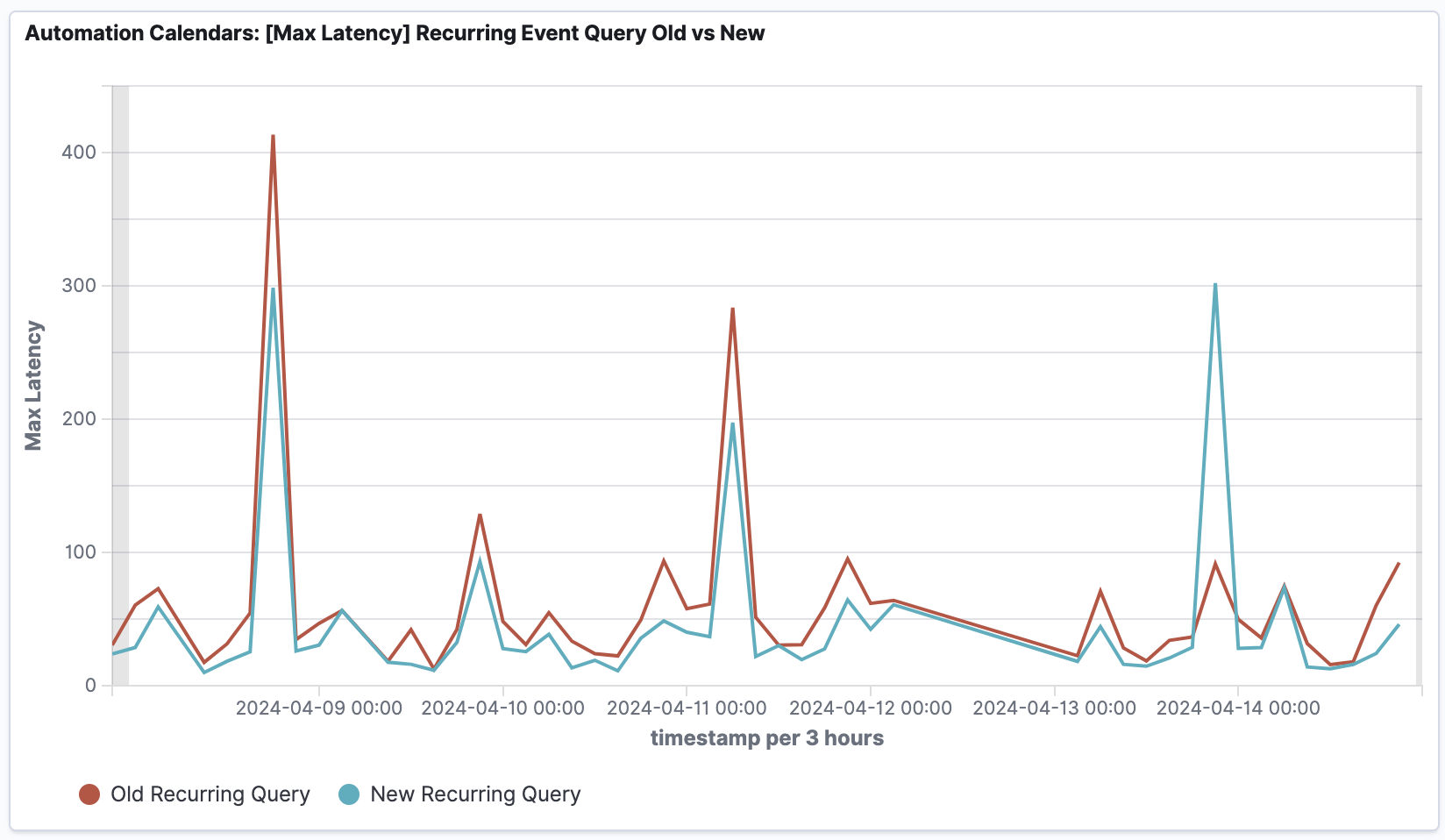
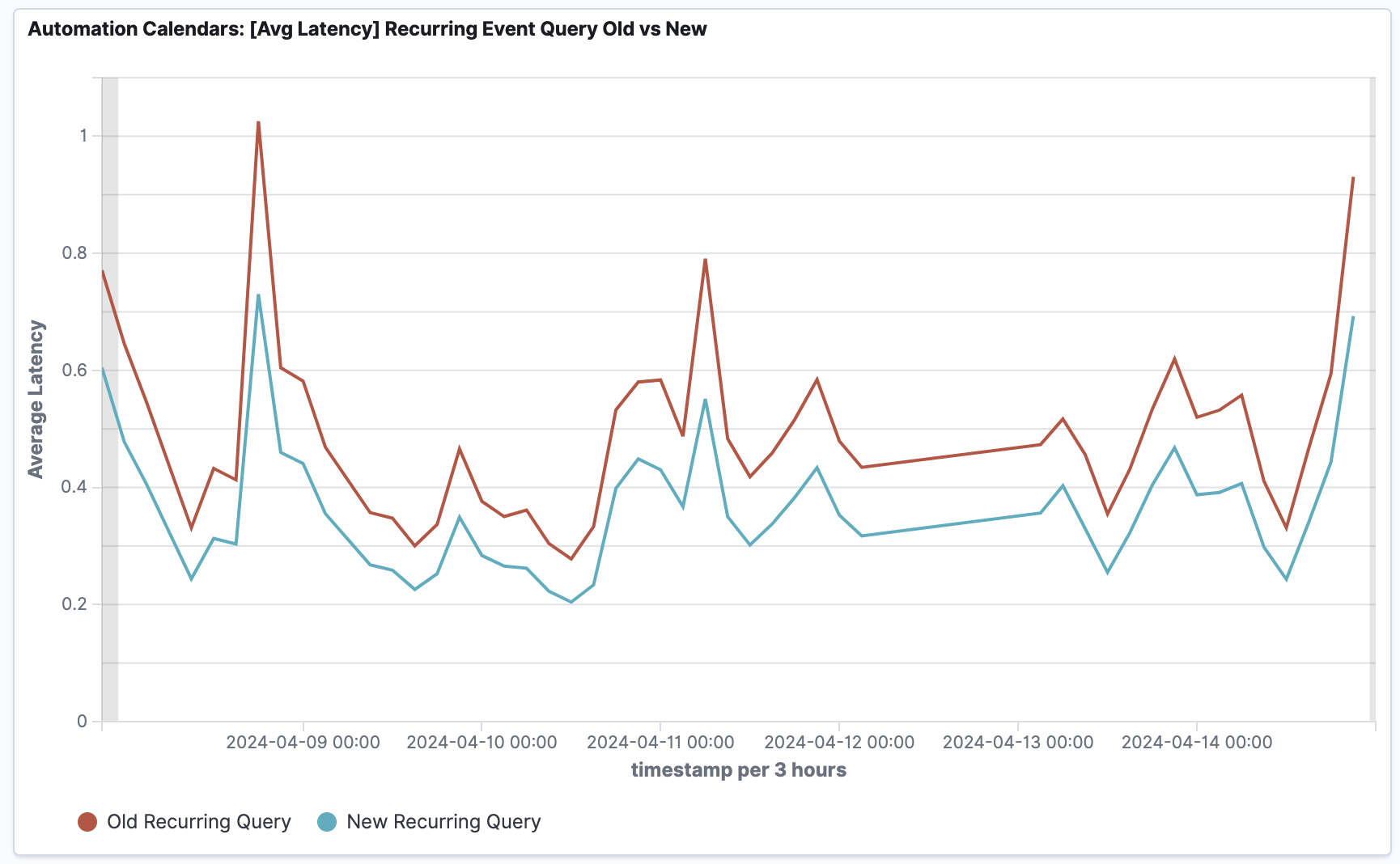
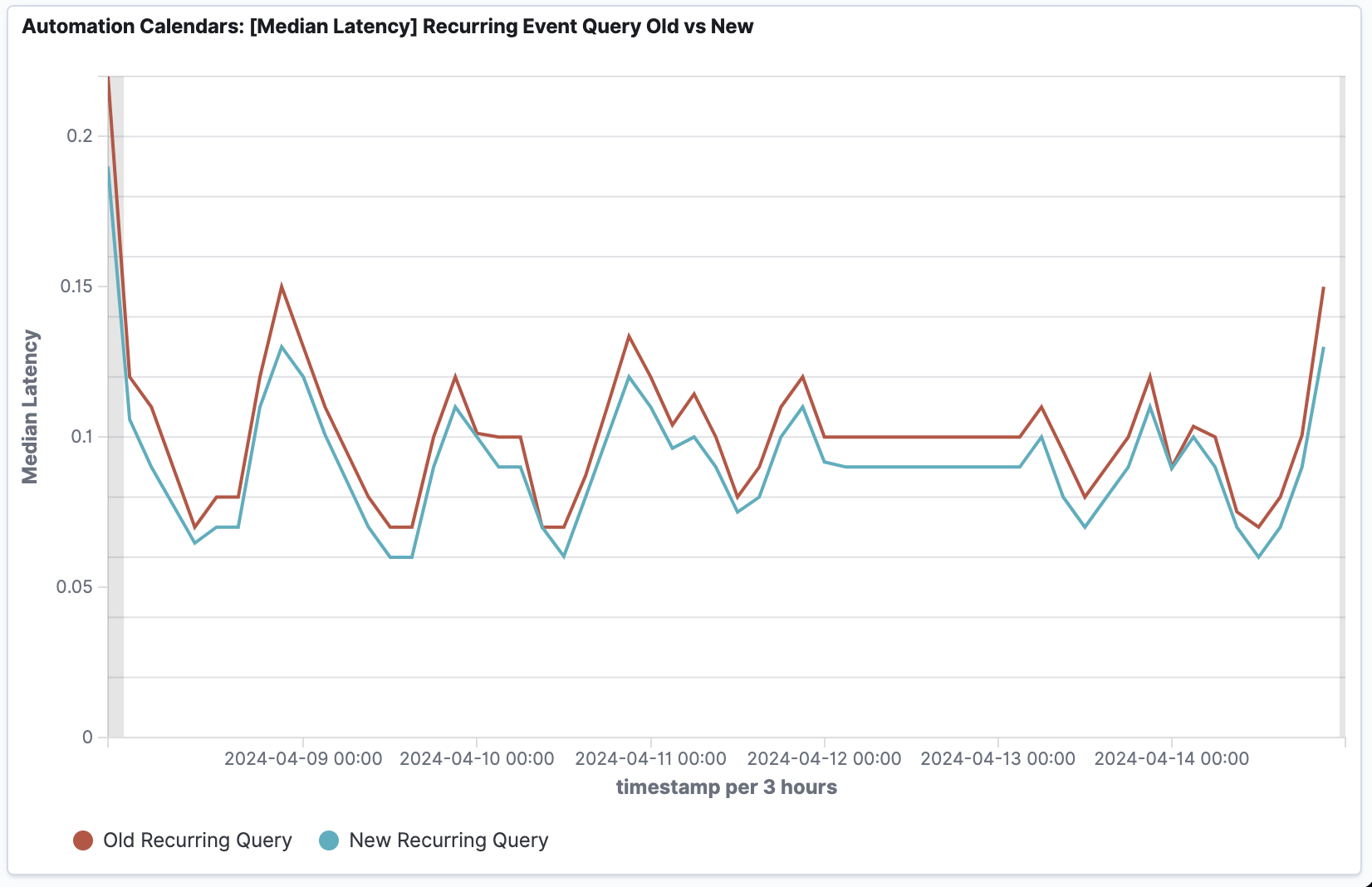
- 48% reduction in Recurring Event reads, from 2.4 billion to ~1.5 billion records per month, resulting in cost savings.
- 46% reduction in Max Latencies, indicating substantial improvements in addressing the most impacted query instances.
- 2% reduction in Median Latencies, signifying enhanced performance across the majority of query instances. Up to 50% improvement for the most affected businesses.
- 23% reduction in Average Latencies, showcasing overall improvement in the query response times.
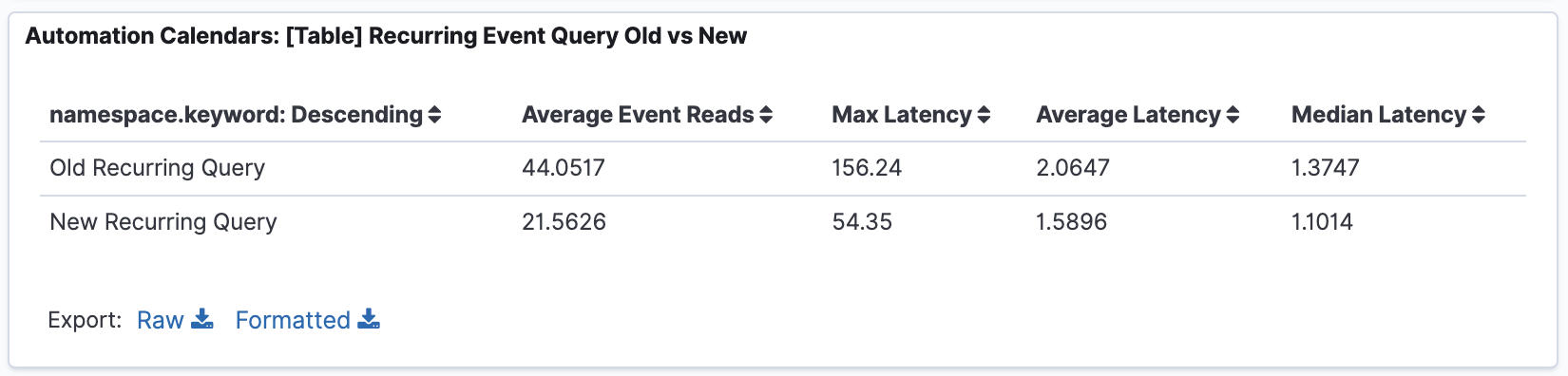 This table shows the improvement metrics
This table shows the improvement metrics
Conclusion
In a nutshell, by identifying the problem, understanding the nuances of recurring events, thinking creatively, and implementing simple yet effective solutions, we’ve made scheduling faster, smoother, and more cost-effective.